What is Answer Engine Optimisation and Why Does It Matter Now?
The rules of search visibility are changing in ways that cannot be ignored. Google AI Overviews, which now appear on roughly 13 to 20 percent of all search queries, synthesise information from multiple sources and present a single, authoritative response at the top of the results page. Rather than returning a ranked list of blue links and inviting the user to click through, these AI-generated summaries answer the question directly. Your content either contributes to that answer, or it does not exist in the user's journey.
This is the core challenge that Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO) addresses. Where traditional SEO focuses on earning a high position in the search engine results page (SERP), AEO focuses on being selected as a cited source within an AI-generated response. The distinction matters because, according to Pew Research Centre data published in 2025, when an AI Overview is shown, users click through to traditional results roughly half as often as they would otherwise. Your content can still drive brand awareness and influence purchasing decisions without ever receiving a direct click.
Research from Surfer SEO illustrates the commercial implication well: Ahrefs reported that 0.5 percent of its visitors in a given month arrived from AI search, yet those visitors accounted for 12.1 percent of all new sign-ups, representing a conversion rate 23 times higher than traditional organic search. AEO-driven traffic, when it does arrive, brings significantly higher purchase intent.
This guide provides the tactical framework to optimise for Google AI Overviews specifically. It assumes you already understand foundational SEO concepts, including crawlability, keyword research, on-page optimisation, and link building, and builds directly on top of those foundations.
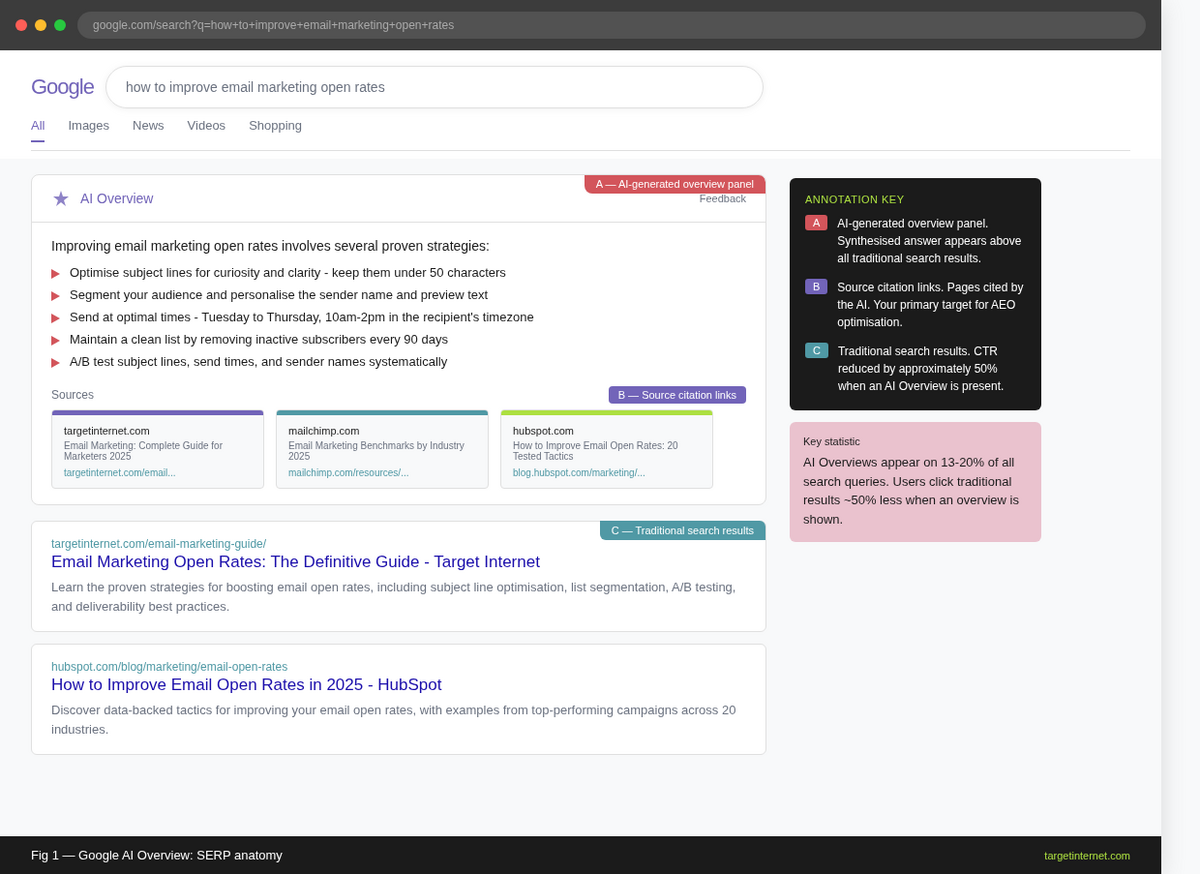
A Google AI Overview appearing at the top of a SERP for a how-to query, with source citations visible beneath the generated text. Label the overview panel, the source links, and any rich result elements below.
How Google AI Overviews Select Sources
Before optimising, you need to understand the selection mechanism. Google AI Overviews are powered by the Gemini model and use a process sometimes described as "query fan-out," in which the system generates multiple sub-queries from a single user search, retrieves pages relevant to each sub-query, and synthesises the results into a coherent answer. This means a single AI Overview can draw from several different pages, each contributing a specific piece of information.
Several factors influence whether a page is selected as a source.
First, the page must already be indexed and discoverable via Google's standard crawling infrastructure. AI Overviews do not operate on a separate index. If your page has crawlability issues, it will not appear regardless of content quality.
Second, the content must be perceived as authoritative and trustworthy within its subject area. Google applies its E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) as a quality signal. Pages with strong E-E-A-T signals are disproportionately likely to be cited.
Third, research from multiple practitioners suggests that approximately 82 percent of AI Overview citations come from deep, topic-specific URLs rather than homepages or category pages. The implication is significant: specialist resource pages and well-structured long-form content are more likely to be cited than broader hub pages.
Fourth, content structure directly affects whether the AI can extract a clean, usable response from your page. Google's systems parse natural language, but they extract far more reliably from content that is logically ordered, uses clear headings, and provides direct answers at the start of each section.
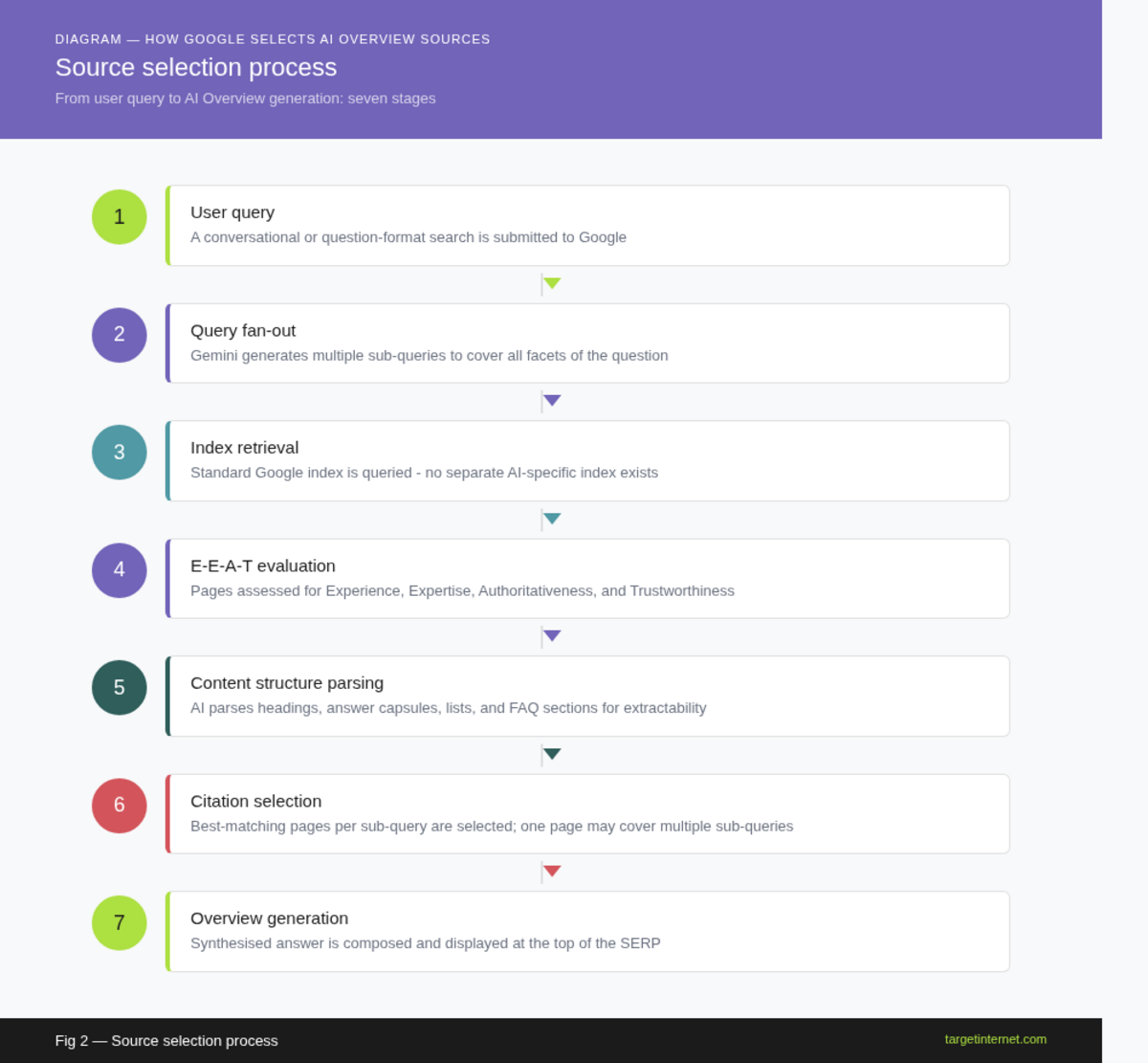
A flowchart illustrating the Google AI Overview source selection process: User Query > Query Fan-Out (multiple sub-queries) > Index Retrieval > E-E-A-T Evaluation > Content Structure Parsing > Citation Selection > Overview Generation. Use numbered steps and directional arrows.
Step 1: Build a Query-Led Content Strategy
AEO begins not with content creation but with query research. The key distinction from conventional keyword research is that you are mapping conversational, intent-rich queries rather than isolated keywords.
Identify the question layer of your topic. Tools such as AnswerThePublic, Semrush's Keyword Magic Tool, and Ahrefs' Keywords Explorer all surface question-based queries. Prioritise queries that begin with "what," "how," "why," "which," and "can." These naturally correspond to the types of prompts that trigger AI Overviews.
Mine Google's own SERP features. The People Also Ask (PAA) section is one of the most reliable indicators of what Google considers a sub-question within a topic cluster. Export PAA questions systematically using tools such as AlsoAsked or by exporting results from your SEO platform. Each PAA question is a potential AEO content opportunity.
Target longer, more specific queries. Analysis from Single Grain found that queries of eight or more words are approximately seven times more likely to trigger an AI Overview than shorter queries. Long-tail, conversational queries are your highest-priority targets.
Prioritise queries with informational intent. AI Overviews appear most consistently on informational and navigational queries. Transactional queries, those with high commercial intent such as "buy," "price," or "discount," are less likely to trigger an AI Overview, so informational content that supports the early and mid-stages of the buying journey is where your AEO effort should be concentrated.
Map queries to content gaps. Conduct an audit of your existing content to identify which of your target queries already have dedicated, well-structured pages and which do not. Gaps represent quick wins; existing content that ranks but is poorly structured for AI extraction represents optimisation opportunities.
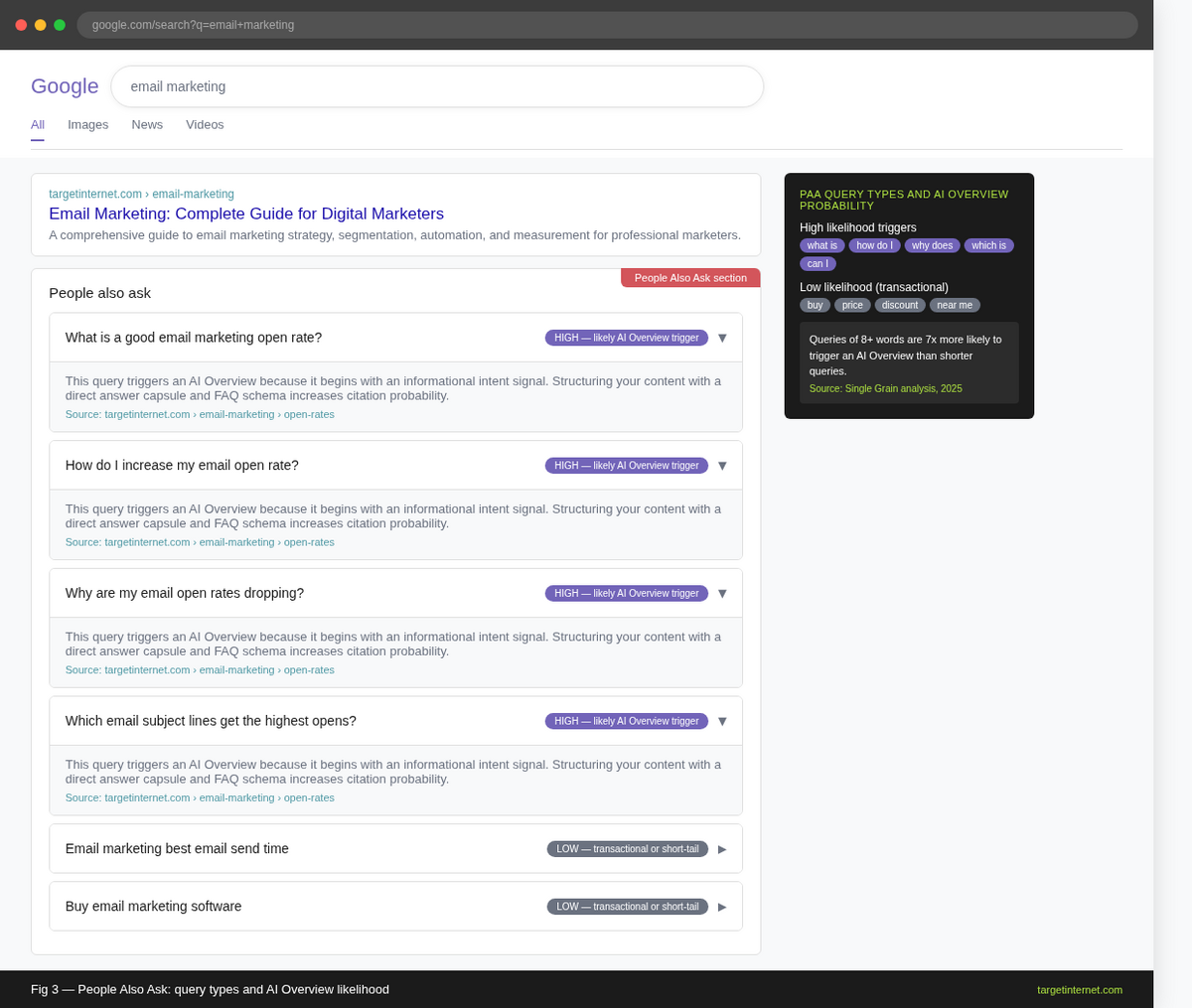
A Google SERP showing the People Also Ask section expanded for a broad informational query. Label each PAA question and indicate which types are likely to trigger AI Overviews.
Step 2: Structure Your Content for AI Extraction
This is the most operationally critical step in AEO. The way your content is physically structured on the page determines whether a language model can reliably identify and extract the precise information it needs to answer a sub-query.
Lead with a direct answer. Known as the inverted pyramid model, this approach places the most important information first. Practitioners and Google's own guidance recommend beginning every major section with a concise, declarative answer in two to four sentences before expanding into supporting detail. Aim for a 50 to 70-word summary at the top of each article that directly addresses the primary query.
Use H2 and H3 headings as questions. Where appropriate, frame your subheadings as the questions your audience would ask. This mirrors the conversational structure of AI queries and improves the chances that Google can match your content to specific sub-queries within the fan-out process. For example, rather than using "Benefits of Content Audits" as a heading, use "What are the benefits of conducting a content audit?"
Write in short, declarative sentences. Keep paragraphs to two or three sentences at most. Surfer SEO's analysis of AI Overview inclusions found that AI-generated answers include unordered or ordered lists 78 percent of the time, which reflects the preference for scannable, extractable formats.
Use lists, tables, and structured comparisons. These formats package information in a form that AI models can easily parse and incorporate into responses. Use ordered lists for step-by-step processes, unordered lists for feature sets or options, and tables for comparisons or specification sets. If your content involves any kind of "X versus Y" framing or "best options for" evaluation, a structured table is almost always the right format.
Include an FAQ section. A dedicated FAQ section at the end of substantive pages serves multiple purposes: it maps directly to PAA queries, it provides the concise Q&A format that AI models extract reliably, and it is the most direct way to implement FAQPage schema markup, which is covered in Step 4.
Keep sentences under 20 words where possible. This is not about dumbing down the content; it is about reducing syntactic complexity so that both readers and language models can extract meaning without ambiguity.
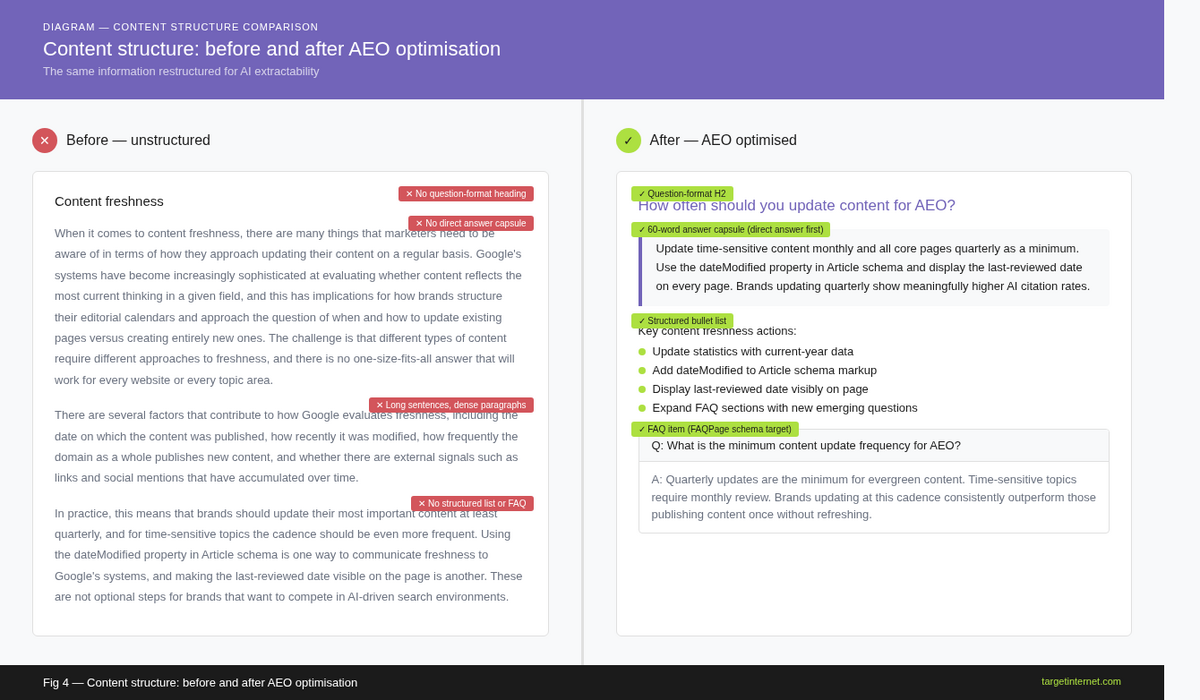
A side-by-side comparison of two versions of the same content block. The left version shows dense paragraphs with no headings. The right version shows the same information restructured with a question-format H2, a 60-word answer capsule, a bullet list, and an FAQ item. Label each structural element.
Step 3: Strengthen E-E-A-T Signals Across Your Site
Google's AI Search Guidelines, updated in 2025, reaffirm that Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness remain the primary quality framework. For AI Overviews, these signals are particularly important because the system needs to determine not just whether your content answers a query, but whether your content is the right source to cite.
Build credible author profiles. Every substantive piece of content should be attributed to a named author. That author should have a dedicated bio page that includes verifiable credentials, links to professional profiles such as LinkedIn, relevant qualifications, publications or industry affiliations, and any awards or recognition. The bio page should itself be internally linked from every article the author has written.
Use Person schema on author pages. Implementing Person schema, discussed further in Step 4, makes the author's credentials machine-readable, allowing Google to match the author to its Knowledge Graph and strengthen the E-E-A-T signal associated with their content.
Cite external sources within your content. Linking out to authoritative third-party sources, such as peer-reviewed research, government data, or industry reports, is a signal of editorial diligence. It demonstrates that your content is grounded in verifiable information rather than unsupported claims.
Earn external mentions and citations. Being referenced in industry publications, trade press, and authoritative third-party sites strengthens your topical authority. This overlaps with traditional link building but extends to unlinked brand mentions, podcast appearances, and contributed articles.
Display trust signals on the page. Publication dates, last-updated dates, reviewer credits for technical or medical content, and transparent methodology notes all contribute to the trustworthiness dimension of E-E-A-T. Make these elements visible and machine-readable.
For YMYL content, apply the highest standard. "Your Money or Your Life" content, covering topics in health, finance, legal services, and related areas, is subject to a significantly higher E-E-A-T threshold. If your brand operates in these categories, author credentials, external peer review, and citation of primary sources are not optional.
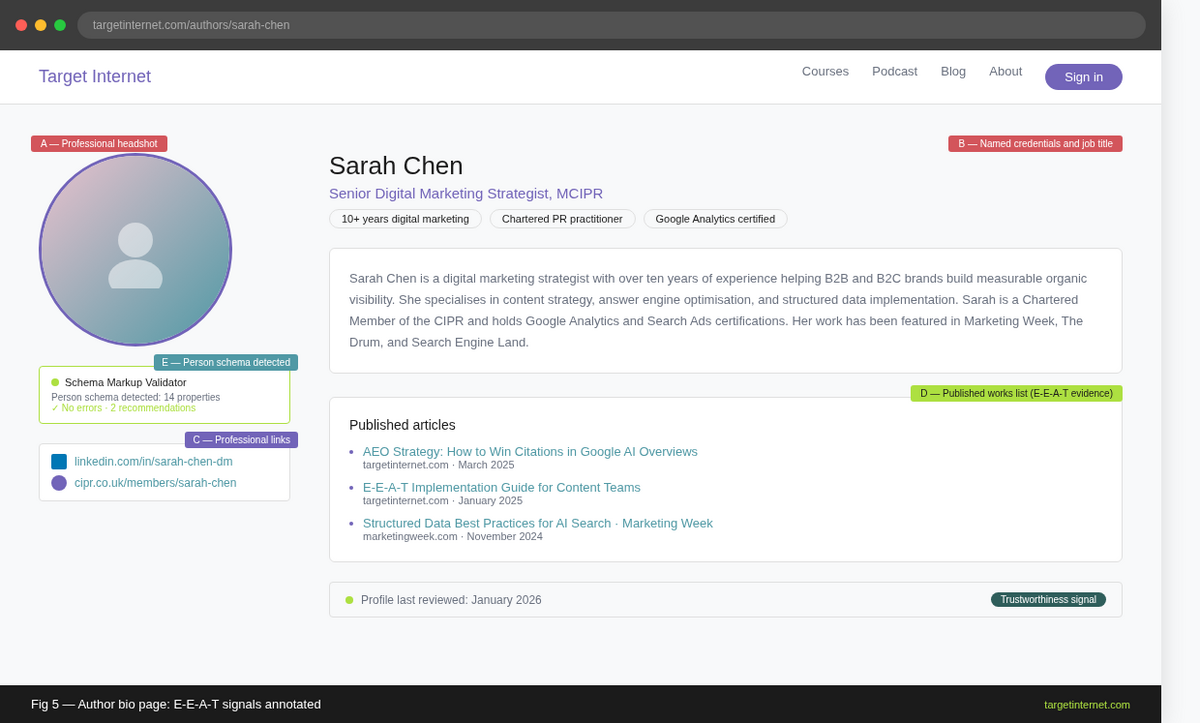
An example author bio page with annotations highlighting the key E-E-A-T elements: professional headshot, named credentials, links to LinkedIn and professional body, list of published work, and a Person schema badge indicator from a browser extension such as Schema Builder.
Step 4: Implement Schema Markup Strategically
Structured data is the mechanism by which you communicate your content's meaning, structure, and authority directly to Google's systems in a machine-readable format. Google's official documentation recommends JSON-LD as the preferred implementation format because it is embedded in the page's head rather than interwoven with the HTML, making it easier to maintain at scale.
It is important to set realistic expectations here. Google does not guarantee that schema markup will result in AI Overview citations, and no schema type acts as a direct admission ticket. Schema reduces ambiguity, strengthens entity understanding, and increases eligibility for rich results, which in turn improves the probability of AI Overview inclusion. Treat it as a force multiplier applied to content quality, not a shortcut.
The following schema types are of highest priority for AEO.
FAQPage schema. Apply this to any page that contains a dedicated question-and-answer section. It directly signals to Google that your content is structured to answer specific questions, which aligns with the query fan-out process used by AI Overviews. Ensure that the questions and answers in your schema match the visible content on the page exactly.
HowTo schema. For any step-by-step guide or instructional content, HowTo schema provides clear step labels, supply and tool references, and time estimates. This is especially effective for process-oriented queries that commonly trigger AI Overviews.
Article schema. Apply this to all blog posts and editorial content. It specifies the publisher, author, date published, and date modified. The dateModified property is particularly important for signalling content freshness.
Organization schema. Implement this sitewide in the head of every page. It establishes your brand as an entity in Google's Knowledge Graph by providing your official name, URL, logo, founding date, and social media profile URLs via the sameAs property. This is your foundational trust anchor.
Person schema. Apply this to all author bio pages. Include name, job title, employer, credentials, and links to verified profiles. In YMYL categories, this is effectively mandatory.
BreadcrumbList schema. Helps Google understand site structure and can improve the presentation of your URL within search results, including within AI Overview source links.
The practical implementation process is: identify your page type, select the appropriate schema, write the JSON-LD block, embed it in the page head, and validate it using Google's Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator. After deployment, monitor the Rich Results report within Google Search Console to confirm Google is successfully reading the markup.
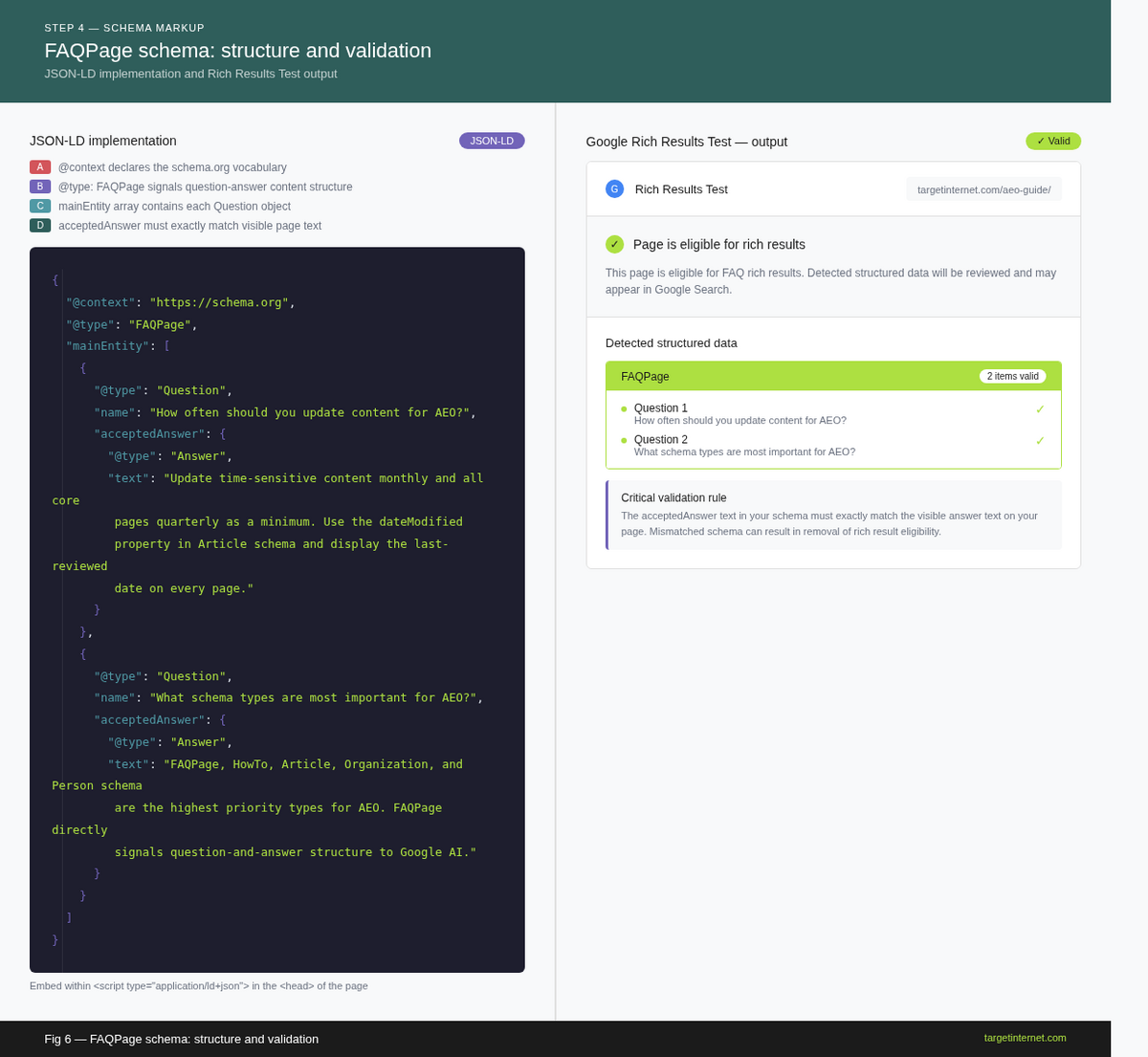
A JSON-LD code block showing a correctly formatted FAQPage schema implementation, with the @context, @type, mainEntity, and acceptedAnswer properties visible. Beneath it, show the corresponding validated output in Google's Rich Results Test tool.
Step 5: Build Topical Authority Through Content Clusters
Google's AI Overviews are significantly more likely to cite sites that demonstrate comprehensive coverage of a topic rather than sites with a single strong page in isolation. This aligns with the established pillar-and-cluster content model but takes on added importance in an AEO context because the AI's fan-out process generates multiple sub-queries, each of which requires a dedicated authoritative source.
Map your core topics. Identify three to six primary subject areas where your brand can credibly claim expertise. These become your pillar topics, each supported by a comprehensive, long-form pillar page that provides an authoritative overview of the subject.
Create cluster content for every sub-question. For each pillar topic, produce ten to fifteen cluster articles addressing specific sub-questions, use cases, comparisons, and related concepts. Each cluster article deepens topical coverage and provides the AI with additional citation candidates across multiple sub-queries generated from a single user search.
Interlink deliberately and consistently. Every cluster article should link back to its pillar page and to related cluster articles where relevant. This internal linking architecture signals topical coherence to Google's algorithms and distributes page authority through the cluster.
Maintain content freshness. Brands that perform well in AI citations update their content quarterly at minimum. For time-sensitive topics, this cadence should be monthly. Use the dateModified property in your Article schema to signal updates, and make the last-reviewed date visible on the page. When refreshing, update statistics, replace outdated references, and expand sections where new questions have emerged.
Publish content that is difficult to replicate. Original research, proprietary data, unique case studies, and firsthand expert commentary give Google's AI a reason to cite your source specifically rather than a competitor's similar page. If you have access to customer data, survey results, or internal benchmarks, publish them. These are citation-worthy assets that no competitor can duplicate.
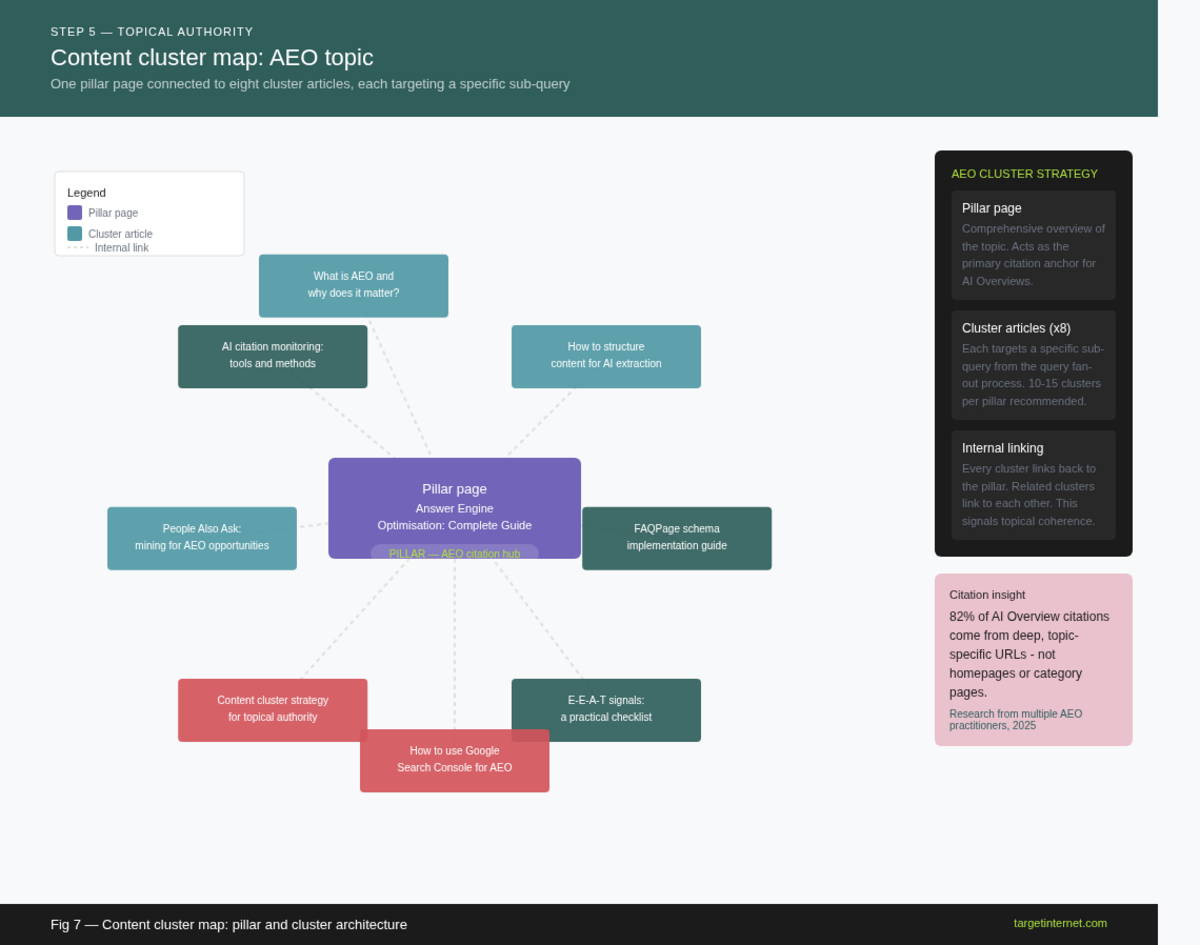
A visual content cluster map showing one central pillar page connected by directional lines to eight surrounding cluster articles. Each cluster article is labelled with an example question-format title. Internal links are shown as two-directional arrows between cluster articles. Label the pillar page and note its relationship to AI Overview citation potential.
Step 6: Optimise Technical Foundations for AI Crawlability
All content strategy is undermined if Google cannot crawl and render your pages effectively. Several technical factors have specific relevance to AI Overview inclusion.
Avoid JavaScript-heavy page rendering for key content. Google's AI crawlers may struggle to parse JavaScript-rendered content. Ensure that the most important textual content, including your answer capsule, FAQ sections, and key headings, is delivered in clean HTML rather than injected via client-side JavaScript. If you use a JavaScript framework such as React or Vue, configure server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation for your priority pages.
Ensure pages load quickly and pass Core Web Vitals. Page experience remains a quality signal. Slow loading times and poor performance on Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Interaction to Next Paint (INP) metrics can reduce your pages' perceived quality and therefore their citation probability.
Use semantic HTML correctly. Proper use of H1, H2, and H3 tags, as well as HTML5 sectioning elements such as article, section, and main, helps Google's parsers understand the hierarchical structure of your content. Do not use heading tags for stylistic purposes; use them to represent genuine information hierarchy.
Check your robots.txt and crawl budget. Confirm that your highest-value AEO content pages are not blocked in your robots.txt file and are not excluded from indexing via noindex directives. Conduct a regular crawl audit using tools such as Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify crawl errors on priority pages.
Submit and maintain your XML sitemap. Ensure all priority AEO content pages are included in your XML sitemap and that the sitemap is submitted to Google Search Console. For high-priority content updates, use the URL Inspection tool to request re-indexing promptly after publication.
Enable HTTPS sitewide. This is a baseline requirement. Any content served over HTTP will be deprioritised as a citation candidate given the trust implications of an unsecured connection.
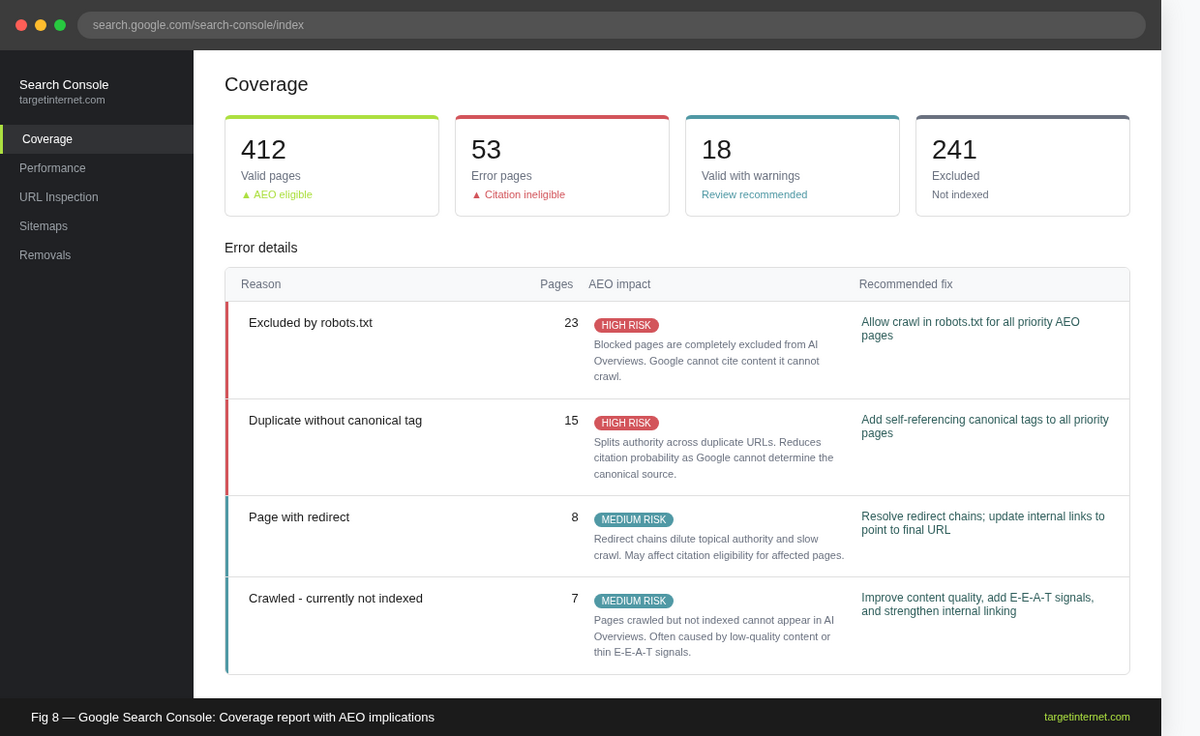
Google Search Console's Coverage report filtered to show pages with indexing errors on a sample site. Annotate the different error types, such as Excluded by robots.txt, Page with redirect, and Duplicate without canonical, and note their AEO implications.
Step 7: Extend Visibility Beyond Your Own Domain
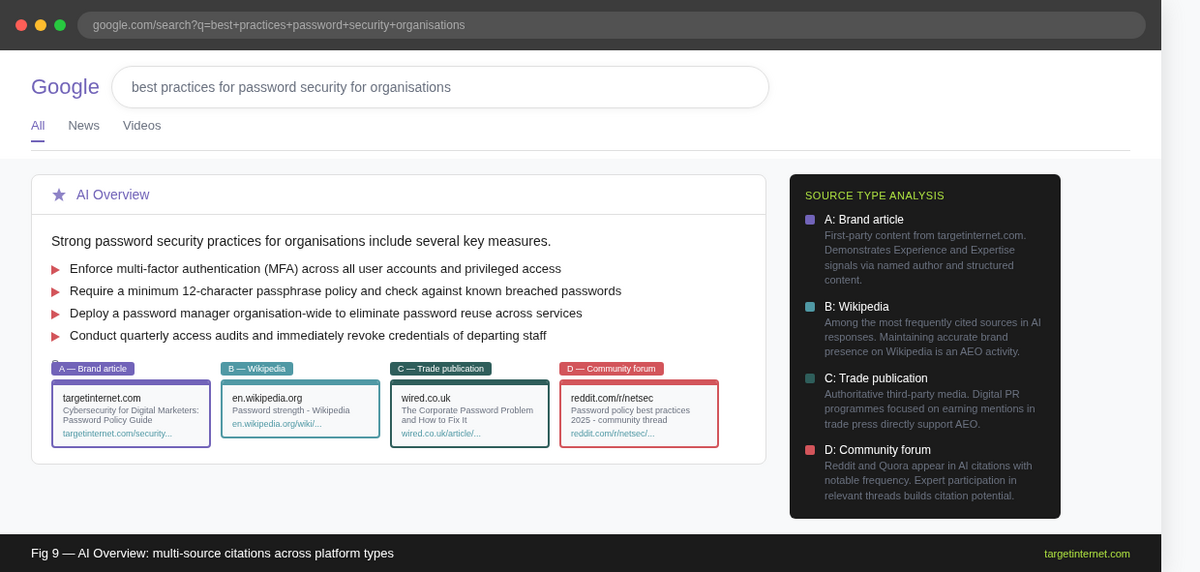
One of the most often overlooked dimensions of AEO is that Google AI Overviews do not exclusively cite first-party brand content. They aggregate information from across the open web, which means your brand's presence on third-party platforms, directories, forums, and publications contributes to the probability of AI citation.
Build and maintain a Google Business Profile. For queries with local or brand intent, Google Business Profile data is surfaced within AI Overviews. Ensure your profile is complete, regularly updated, and reflects accurate information including categories, services, and attributes.
Claim and optimise your presence on Wikipedia and Wikidata. Wikipedia remains one of the most frequently cited sources in AI-generated responses across all platforms. If your brand, product, or key personnel merit a Wikipedia entry, maintaining accuracy and appropriate referencing within that entry is an AEO activity. Wikidata, which provides the structured entity database underlying Google's Knowledge Graph, is equally important for ensuring your brand is correctly represented as an entity.
Pursue mentions in industry publications. Being cited in trade publications, respected media outlets, and industry reports builds the external authority signals that Google weighs when selecting AI Overview sources. This is the intersection of traditional PR and AEO. A structured digital PR programme focused on earning mentions, not just links, in authoritative publications is one of the highest-leverage AEO activities available to content and brand teams.
Engage constructively on forums and Q&A platforms. Reddit and Quora feature in AI Overview citations with notable frequency. Where your team can provide genuinely useful, expert responses to relevant questions in these forums, doing so builds both brand presence and citation potential.
Step 8: Measure AEO Performance and Build a Feedback Loop
Measurement in AEO is more complex than tracking keyword rankings because AI Overview appearances are not yet consistently reported in standard analytics platforms. However, a combination of available tools and manual monitoring methods enables you to build a working measurement framework.
Use Google Search Console as your baseline. While Search Console does not directly label AI Overview impressions separately from standard impressions for all queries, the Queries report surfaces high-impression, lower-CTR patterns that often indicate AI Overview interference. A query showing high impressions and a declining click-through rate over time is likely being answered in an AI Overview without the user needing to click through.
Monitor your target queries manually and systematically. Establish a list of 20 to 50 priority queries aligned with your AEO content strategy. Search these queries from an incognito browser weekly or fortnightly and document whether an AI Overview appears, whether your content is cited, and which source is cited if not yours. Record this in a simple tracking sheet with columns for query, date, AI Overview present (yes/no), your citation (yes/no), and competitor cited.
Use specialist AI visibility tools. A growing number of platforms now provide automated AI Overview monitoring. Tools such as Profound, Semrush's AI Toolkit, and Ahrefs' SERP Features tracking offer varying degrees of AI Overview visibility reporting. These tools allow you to track citation share across a larger query set than manual monitoring permits.
Track featured snippet performance as a leading indicator. There is a strong correlation between earning a featured snippet and being cited in an AI Overview for the same query. Featured snippet performance, which is reportable in Search Console and most SEO platforms, provides a measurable proxy for AI Overview citation readiness. If a piece of content wins a featured snippet, it is a strong signal that the page's structure and authority are aligned with AEO requirements.
Define and track AEO-specific KPIs. Recommended key performance indicators include: the percentage of target queries that trigger an AI Overview; the percentage of AI Overview appearances that include a citation to your domain; brand mention volume in AI responses across platforms; and the conversion rate of sessions attributed to AI referral traffic in your analytics platform.
Establish a quarterly content review cycle. Brands that review and refresh their content quarterly see meaningfully higher AI citation consistency. Use your query monitoring data to identify which pages are being cited, which are being outperformed by competitors, and which queries show an AI Overview that your content does not appear in. Let this data drive your next quarter's content production and optimisation priorities.
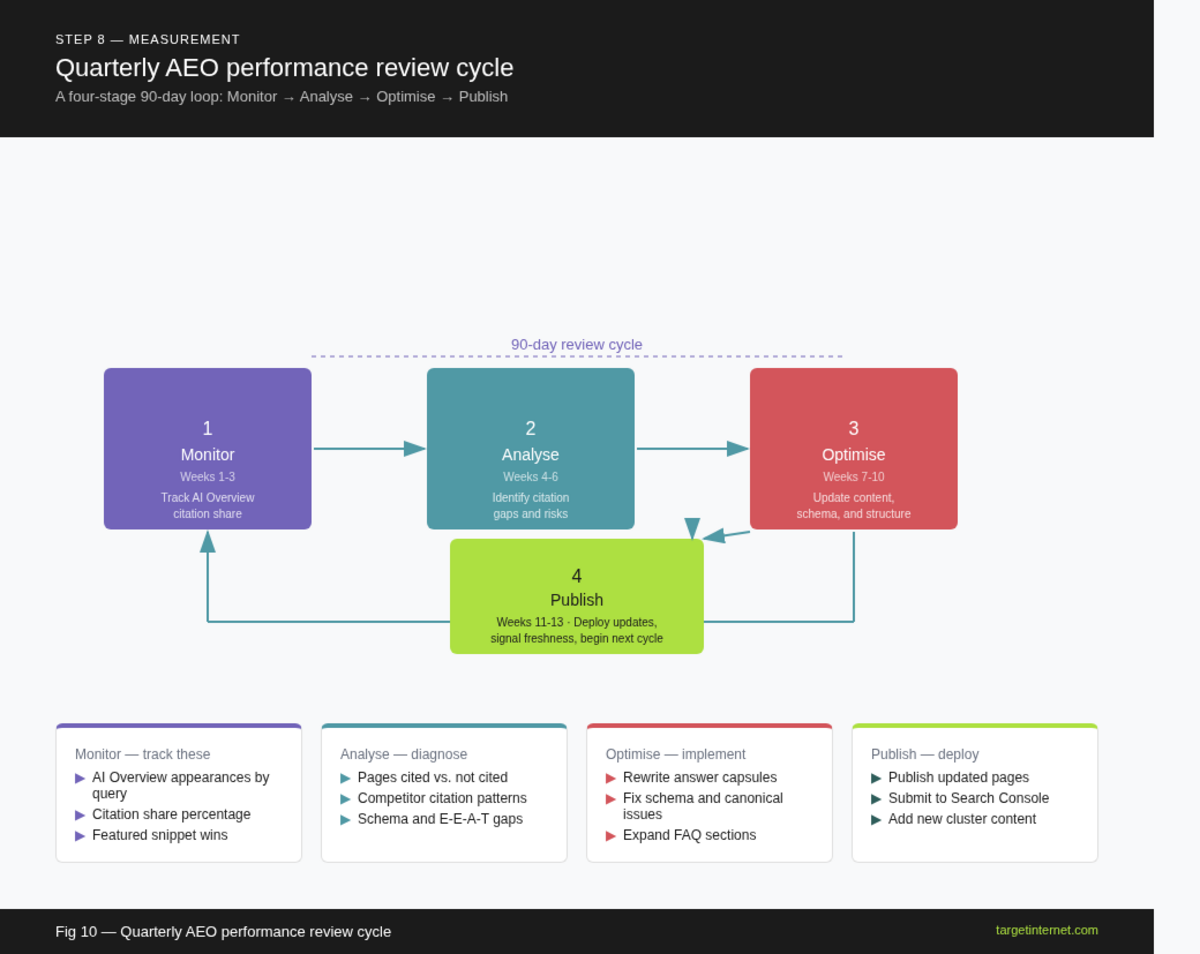
A quarterly AEO performance review cycle shown as a circular process with four stages: Monitor (track AI Overview appearances), Analyse (identify citation gaps and competitor citations), Optimise (update content structure, schema, and freshness), and Publish (add new cluster content targeting uncovered queries). Use arrows connecting each stage in a loop.
Common AEO Mistakes to Avoid
Publishing content without a direct answer at the top is one of the most common errors. If a page takes three paragraphs to arrive at its core response, AI models will often struggle to extract a clean answer and will prefer a competitor's more directly structured page.
Implementing schema markup that does not match the visible content is a critical error. Google's guidelines are explicit that structured data must accurately represent what is on the page. Mismatched schema can result in a manual action or removal of rich result eligibility.
Focusing exclusively on head terms rather than long-tail question queries misses the queries most likely to trigger AI Overviews. Rebalancing your keyword strategy towards conversational, long-tail queries is essential.
Publishing content once and not updating it allows competitors to overtake you with fresher data and more current references. AI systems favour freshness, particularly for topics where information changes over time.
Neglecting third-party platforms leaves significant citation surface area unoptimised. Your own website is one source in a wider ecosystem; building presence across authoritative external platforms expands your citation footprint.
A Note on Staying Ahead as the Landscape Evolves
AEO is not a static discipline. Google continues to expand AI Overview coverage, adjust the types of queries that trigger generative responses, and refine the signals used to select sources. Semrush predicts that LLM-driven traffic will overtake traditional Google search by the end of 2027, suggesting that the balance of effort between conventional SEO and AEO will shift significantly within the near term.
The practitioners who will perform best in this environment are those who treat AEO not as a separate workstream but as an integrated evolution of their existing SEO and content strategy. Strong technical foundations, authoritative content, credible authors, and structured data are not exclusively AEO activities; they are the practices that make content perform well across every surface Google uses to surface information.
Build these habits into your standard operating procedures now, and you will be well positioned regardless of how the specific mechanisms of AI Overviews continue to develop.
Bibliography
Amsive. (2025). Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): Your Complete Guide to AI Search Visibility. https://www.amsive.com/insights/seo/answer-engine-optimization-aeo-evolving-your-seo-strategy-in-the-age-of-ai-search/
Backlinko / Semrush. (2025). Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): How to Win in AI Search. https://backlinko.com/answer-engine-optimization-aeo
BrightEdge. (2025). Structured Data in the AI Search Era. https://www.brightedge.com/blog/structured-data-ai-search-era
Dataslayer. (2025). How to Optimize for Google AI Overviews in 2025. https://www.dataslayer.ai/blog/how-to-optimize-for-google-ai-overviews-in-2025
Digi Solutions. (2025). Schema Markup Best Practices and Key Optimization Strategies. https://digi-solutions.com/schema-markup-best-practices/
Evergreen Media. (2026). Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): AI Visibility in 2025. https://www.evergreen.media/en/guide/answer-engine-optimization/
Geneo. (2025). Schema Markup and Structured Data Best Practices for GEO in AI Search. https://geneo.app/blog/schema-markup-structured-data-best-practices-geo-ai-search-2025/
Google Search Central. (2025). Introduction to Structured Data Markup. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/structured-data/intro-structured-data
Gryffin Media. (2025). Google AI Overviews: How to Rank and Optimize for AI Search. https://www.gryffin.com/blog/google-ai-overviews-ranking-guide
Marketing Illumination. (2025). Best Practices for Answer Engine Optimization: AEO for SEO Visibility. https://www.marketingillumination.com/blogs/best-practices-for-answer-engine-optimization
MYIDCM. (2025). Answer Engine Optimization: Complete Insight into AI-Driven Search Engines. https://www.myidcm.com/blog/answer-engine-optimization
OWDT. (2025). What is Answer Engine Optimization? How AEO Changed SEO. https://owdt.com/article/what-is-answer-engine-optimization/
Profound. (2025). Winning in AI Visibility: A Marketer's Playbook for Answer Engine Optimization. https://www.tryprofound.com/resources/articles/answer-engine-optimization-aeo-guide-for-marketers-2025
SEO Sherpa. (2025). Google AI Search Guidelines: What They Mean for SEO. https://seosherpa.com/google-ai-search-guidelines/
Single Grain. (2025). Google AI Overviews: The Ultimate Guide to Ranking in 2025. https://www.singlegrain.com/search-everywhere-optimization/google-ai-overviews-the-ultimate-guide-to-ranking-in-2025/
Surfer SEO. (2025). What is Answer Engine Optimization? 7 AEO Strategies for 2025. https://surferseo.com/blog/answer-engine-optimization/
The Ad Firm. (2025). Structured Data Tips to Rank in Google's AI Overviews. https://www.theadfirm.net/ranking-in-googles-ai-overviews-structured-data-and-content-layout-tips/
Typeface AI. (2025). What is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)? How to Get Cited by AI Search. https://www.typeface.ai/blog/what-is-answer-engine-optimization-why-aeo-matters
Zensciences. (2025). A Comprehensive Guide to Answer Engine Optimization in the Generative AI Era. https://zensciences.com/blogs/a-comprehensive-guide-to-answer-engine-optimization-aeo-in-the-generative-ai-era/